Acid & Alkaline Wastes Disposal in Singapore
November 16, 2022
At GreenTec Energy Singapore, we assist our clients in the aviation, metal galvanising, and semiconductor industries in sustainably disposing of their liquid chemical waste. Waste acids, alkalis, plating solutions, waste water and other liquid chemical waste can all be safely processed for disposal by our company.
We take the liquid chemical waste from our clients and handle them safely at every step, from collection and neutralisation to disposal and incineration, because chemical waste is dangerous if it leaks into the environment.
In this article, we will discuss more about acid and alkaline wastes and how we process them through neutralisation before discharging the neutralised water into the Public sewer.
What are acid and alkaline wastes?
Before we look at the processes involved in the neutralisation and disposal of acid and alkaline waste, let’s first find out what are classified as acid and alkaline wastes.
Based on pH, it is possible to establish whether a solution is acidic or alkaline. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14 – acidic aqueous solutions at 25 °C have a pH under 7, while alkaline aqueous solutions have a pH above 7. pH level of 7.0 at 25°C is referred to as ‘neutral’. A very strong acid may have a pH below 1, while strong bases may have a pH beyond 14. Therefore, acid and alkaline wastes are defined as chemical wastes with a pH value of less than 6.0 (acid) or greater than 9.0 (alkali), or solid chemical wastes that would attain such values when mixed with water.
Sources of acid and alkali wastes
Many different industries produce acid and alkali wastes. In Singapore, some of these industries include semiconductor manufacturing, aviation and metal galvanising industries. Wastes for disposal tend to be materials contaminated as a result of the process.
In some instances, some chemicals may be disposed of as a result of spillage or off-specification production. In general, acid and alkaline wastes are contaminated with other chemicals, which are often dilutely dispersed in large bodies of water.
Industries likely to generate significant quantities of acid and alkaline waste include:
- Dairy factories
- Freezing works
- Industrial cleaning
- Laundries
- Chemical industry
- Soap/detergent manufacturers and more.
These industries may produce acid or alkaline wastes as mixes or contaminated with other pollutants, which would necessitate a more complicated treatment.
Now that we know what defines acid and alkaline wastes as well as their main sources. Let’s take a look at the steps taken to process the acid and alkaline wastes before they are safely disposed of.
Step 1: Waste collection
At the client's location, we start by gathering liquid chemical waste and deposited them into an ISOtank unit or an Intermediate Bulk Container (IBC) or a drum/ carboy/ pail.
All our transporting vehicles are equipped with the required Hazard Communication (HazCom) labels. Additionally, all our field personnel are Hazmat trained, well-trained in professional safety procedures and have the necessary protective gear and equipment to handle and transport such hazardous waste.
Step 2: Lab analysis & lab analysis
Once the waste arrives at our facility, it will be weighed and each collection's sample is taken to our in-house laboratory to be tested. This enables our in-house chemist to do a treatability study for each incoming liquid waste.
Our process engineer will then work with our production team, based on the lab results. The crew will also make sure that all wastes are safely stored in the interim before production starts.
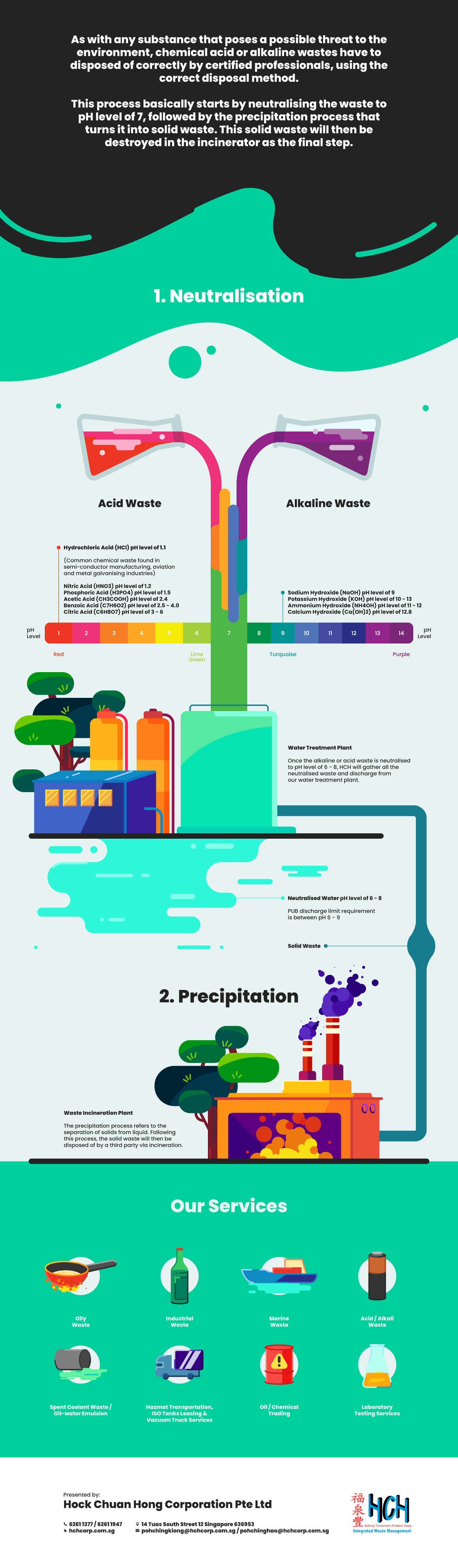
Step 3: Neutralisation of waste acid & alkaline wastes
A supply of alkaline liquid is required to counteract the very acidic wastewater from a cation resin regeneration. The effluent from an anion resin regeneration, which is typically done concurrently, is alkaline. The pH of these two wastewater streams is ‘neutralised’ and approaches 7 when combined. If the combined liquids' pH does not fall within the range that is suitable for discharge, further acid or alkaline must be added to bring the pH within the permissible range.
Typically, the chemicals used to replenish the resins in ion exchange systems are the same compounds used to modify the effluent. The finished mixture then passes through a filter press. The solid precipitate is separated from the neutralised water through this apparatus.
After the neutralisation step, the neutralised wastewater (pH 6.0-8.0) can now be safely discharged. The PUB safe discharge limit is between pH 6.0 to 9.0.
Step 4: Precipitation & incineration of solid waste
Following the neutralisation process, the precipitation process will then separate the solids from the liquid. In the last step, the solids will be disposed of by our third-party partner through incineration.
Conclusion
At GTE, we take pride in ensuring that we do our part in keeping the environment safe through proper waste disposal. If you have any questions regarding liquid chemical waste disposal, be it chemical, waste oil or a mix of waste water, get in touch with us for more information.
 GreenTec Energy Pte Ltd (GTE) is a waste management company located in Tuas, Singapore.
GreenTec Energy Pte Ltd (GTE) is a waste management company located in Tuas, Singapore.
Our service includes Industrial waste, Oily waste, Marine waste.
To provide a hassle free solution to our customer is always the key approach and to ensure a win-win situation towards. As a NEA approved environmental company in Singapore, we take all our services seriously and to ensure maximum safety with compliances applied. Every step of our disposal processes are also designed to meet NEA & SCDF requirements, with latest treatment facilities and laboratories to test and treat all incoming waste before disposal.
GTE operates a total land area of about 100,000sqft at 14 Tuas South Street 12 Singapore 636953. With our comprehensive logistics and transportation fleet, we provide prompt and efficient services in transportation of waste to our premises.



